Skin Disease Assays
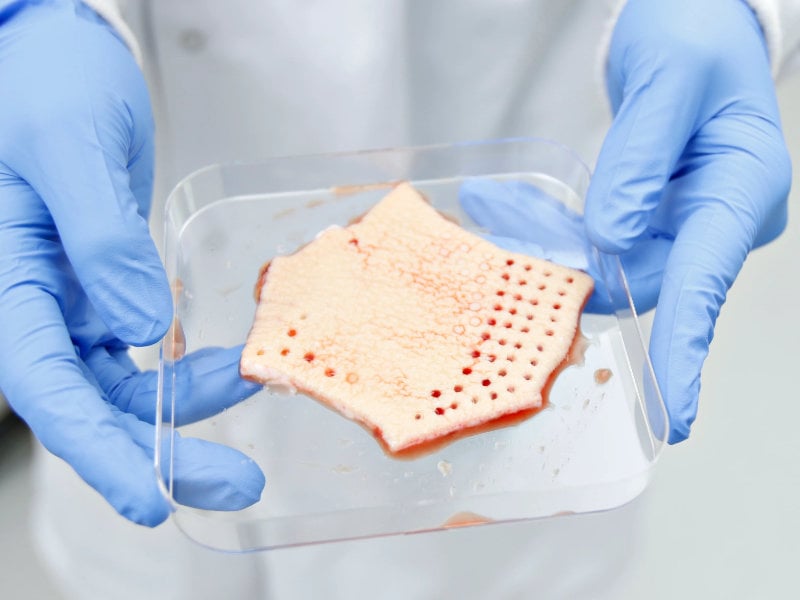
Our human fresh skin disease assays provide the most clinically relevant in vitro assessments of new therapies of any CRO. The pro or anti-inflammatory properties of your test compound can be tested ex vivo using human intact fresh functional skin. Skin tissues are received either as biopsies obtained from patients with psoriasis or atopic dermatitis or, for our higher throughput models, using human fresh skin induced to a disease-relevant inflammatory phenotype, such as our Th17 phenotypic model.
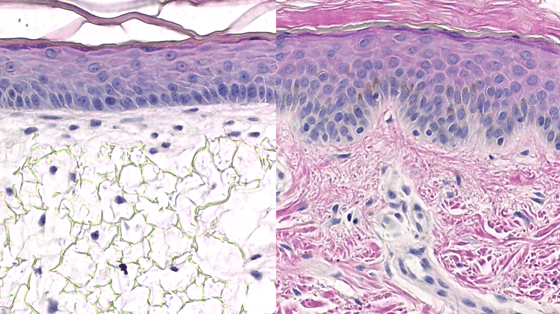
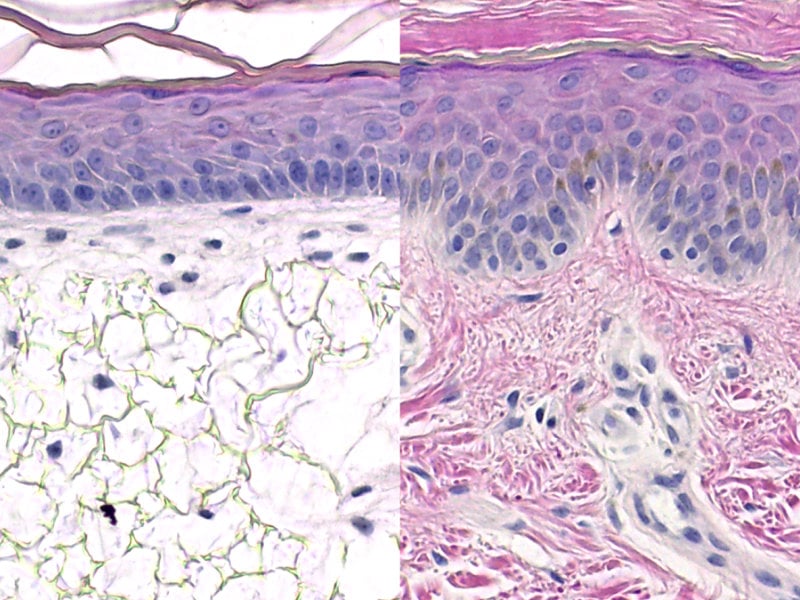
Histological images. Left: Alvetex™ 3D human skin model. Right: real human skin.
Up to 20 test conditions can be assessed using skin from a single donor, allowing for comparatively high throughput and quick turnaround, and your test article can be added to the culture media or applied topically to allow assessment of different formulations. Any resultant changes in inflammatory mediators can be measured via multiplex ELISA/Luminex or via changes in histology or gene expression, using approaches such as RT-PCR or RNA-Seq. We recommend the use of triplicate or quadruplicate biopsies for each test condition to maximise reproducibility and control for any intra-patient variation between individual biopsies.
Our human ex vivo skin assays can be configured to allow either topical (to the epidermal surface) or "systemic" application of compounds (i.e. addition to the culture media). As the skin is cultured at an air-liquid interface the conditions mimic those found in vivo. Our aim is to interfere as little as possible with the native biology of the human skin and retain the complex 3D architecture and mixture of cell types.
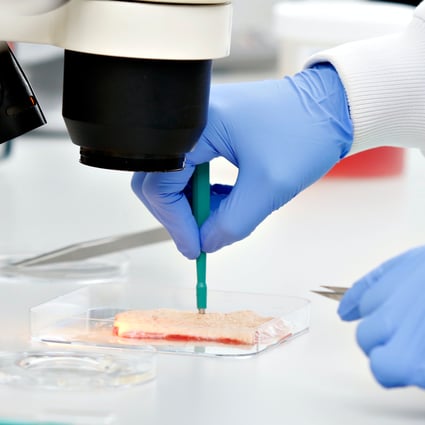
Typically, multiple 3 mm diameter biopsies comprising the full thickness of the skin (epidermis and dermis) are carefully generated prior to set up in culture for up to 24 hours. Various types of formulations can be tested including liquid solutions, creams or gels. Previous projects include the testing of treatments for acne, psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
Please contact our experts today to discuss a customised design for your project.
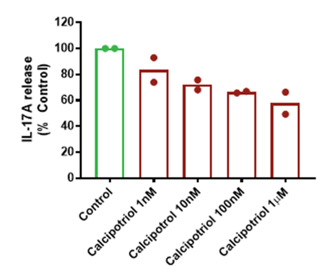
The above figure shows example data from human fresh skin biopsies induced to a create a psoriasis-like phenotype (via a proprietary inflammatory cocktail) and then cultured in the presence or absence of the vitamin D analogue, calcipotriol, which may be used as a treatment for psoriasis. IL-17 is a cytokine implicated in the pathophysiology of psoriasis. Here 1L-17A release from the psoriasis-phenotype skin biopsies has been measured via a Luminex assay, with a concentration-dependent reduction in IL-17A release observed in the presence of calcipotriol (1 nM to 1 mM) when compared to the control levels. The columns show the mean response (from all biopsies) at each concentration; the dots show the mean responses in different donors.





![Wire myography: the ultimate guide [protocol included]](https://www.reprocell.com/hs-fs/hubfs/REPROCELL-04.06.18_0163.jpg?width=756&height=425&name=REPROCELL-04.06.18_0163.jpg)